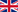
Removal of malignant skin tumors
An nevus, ie a mole, should always be examined by a dermatologist.
An nevus that we think changes color or size should be examined by a dermatologist, who will decide if it needs to be removed or not. In case of benign lesions that the patient wishes to remove, the specialist doctor suggests that removal method that will bring the best aesthetic result.
In case it is necessary to remove a skin lesion, the removal is based on the correct fault management. Since the vast majority of skin tumors appear on the face, a competent skin surgeon can offer the patient an excellent aesthetic result along with the treatment. Since the vast majority of skin tumors appear on the face, a competent skin surgeon can, together with the treatment, offer the patient an excellent aesthetic result..
The pillars of the right treatment:
- Quick diagnosis
- Early identification and intervention
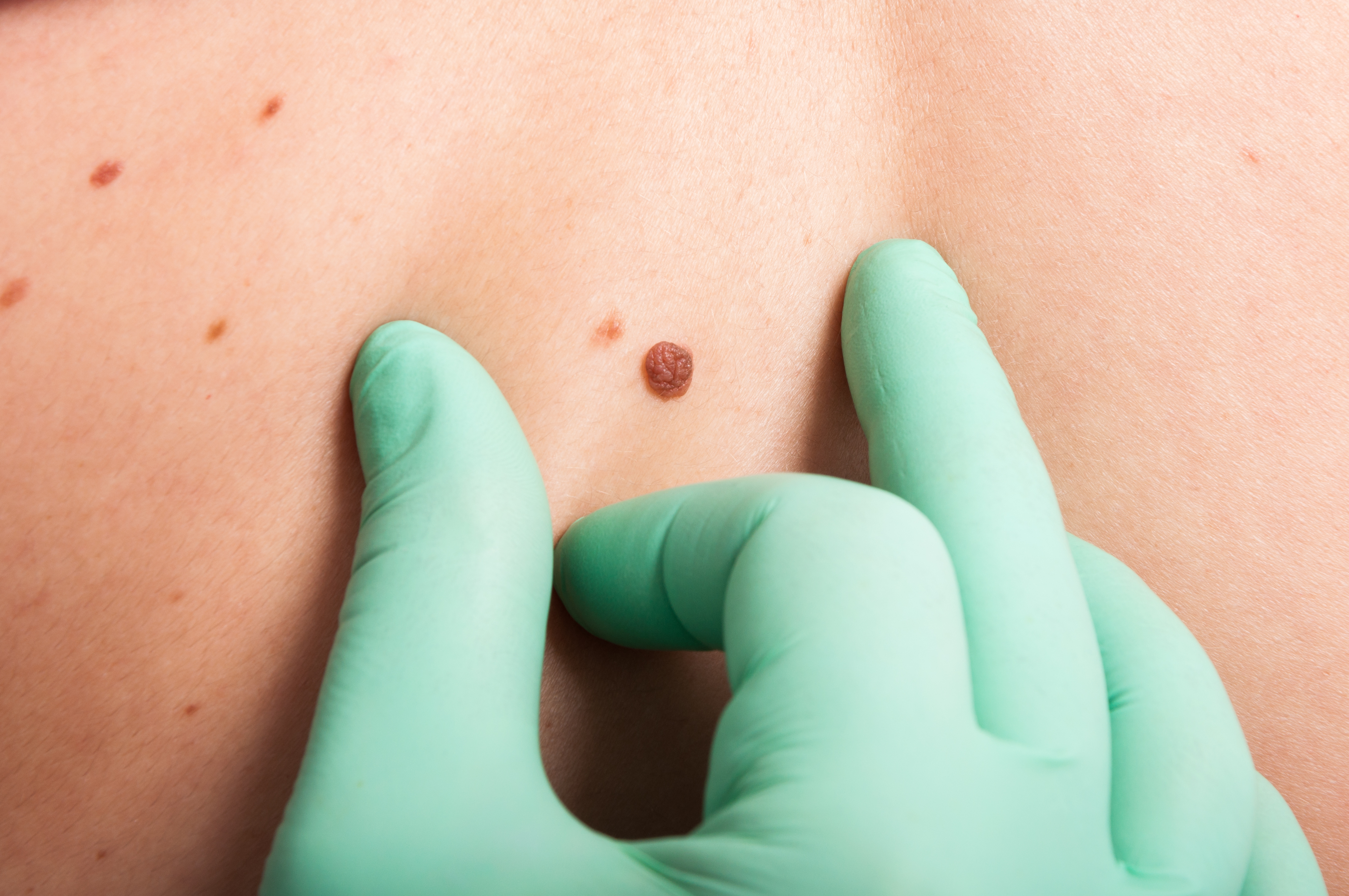
Symptoms and diagnosis
There are 4 main types of skin cancer:
- Basal cell carcinoma. The basal cells are the round cells located in the lower epidermis. About 80% of skin cancers grow from this type of cell. These cancers are described as basal cell carcinomas. Stem cell carcinoma most often develops on the head and neck, although it can be found anywhere on the skin. It is mainly caused by sun exposure or develops in people who have received radiation therapy as children. This type of skin cancer usually develops slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
- Squamous cell carcinoma. Most of the skin is made up of layers, called squamous cells. About 20% of skin cancers grow from these cells and these cancers are called squamous cell carcinomas. Squamous cell carcinoma is mainly caused by sun exposure, so it can be diagnosed in many areas of the skin. It can also grow on skin that has been burned, damaged by chemicals or exposed to X-rays.Squamous cell carcinoma is usually found on the lips, in long-lasting scar sites, and on the skin outside a woman's mouth, anus, and vagina. About 2% to 5% of squamous cell carcinomas spread to other parts of the body, making them more likely to spread from basal cell carcinoma.
- Merkel cell cancer. Merkel cell cancer is an extremely aggressive, or fast-growing, rare cancer. It starts in hormone-producing cells just below the skin and in the hair follicles. It is usually found in the head and neck area. Merkel cell cancer can also be called neuroendocrine skin cancer.
- Melanoma. Where the skin meets the skin, there are scattered cells called melanocytes. These cells produce the pigment melanin, which gives the skin its color. Melanoma starts in the melanocytes and is the most serious type of skin cancer.
Treatment
The removal of skin tumors is preceded by the clinical and dermatoscopic evaluation of the lesions, so as to select the most appropriate way of their removal. Removable lesions are always sent for histological examination, regardless of whether they are benign or malignant tumors. The removal is always done under local anesthesia and the patient returns home after a while. The sutures are removed in 1-2 weeks.